Hot forging aluminum is a critical manufacturing process used to produce high-strength, durable, and lightweight components for various industries. This technique involves heating aluminum to a specific temperature, making it more malleable before applying high-pressure force to shape it into the desired form. Compared to other metalworking techniques, aluminum hot forging offers superior mechanical properties, improved structural integrity, and enhanced resistance to wear and fatigue. The process of aluminum hot forging is widely used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, construction, and electronics, where strong yet lightweight components are essential. By leveraging the benefits of hot forging, manufacturers can produce complex aluminum parts with high precision and minimal material waste.
The Hot Forging Process for Aluminum
The aluminum hot forging process involves multiple steps to ensure the final component meets strict quality and performance standards. The key steps in the process include:
Material Selection and Preparation
Before forging begins, manufacturers select the appropriate aluminum alloy based on the required strength, corrosion resistance, and application needs. Common alloys used in hot forging include 6061, 7075, and 2024 aluminum, which offer excellent mechanical properties. The selected aluminum billet or ingot is then cut to the required size and preheated to the optimal forging temperature.
Heating the Aluminum
Unlike cold forging, which is performed at room temperature, hot forging aluminum requires the metal to be heated to a temperature range of 370°C to 520°C (700°F to 968°F). Heating softens the aluminum, making it easier to shape while reducing the risk of cracking or defects during forging.
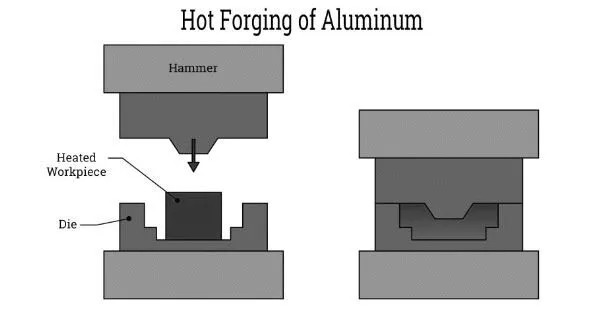
Forging Process
Once heated, the aluminum billet is placed into a forging die, where high-pressure force is applied using a hydraulic or mechanical press. The forging die contains a pre-designed cavity that shapes the aluminum into the desired form. Depending on the complexity of the part, single or multiple forging operations may be required to achieve the final geometry.
Trimming and Machining
After forging, excess material or flash is removed from the aluminum hot forging component through a trimming process. In many cases, additional CNC machining is performed to achieve tighter tolerances, precise dimensions, and smooth surface finishes.
Heat Treatment and Surface Finishing
To enhance the mechanical properties of the forged aluminum part, heat treatment processes such as T6 tempering or annealing are applied. This improves hardness, strength, and durability. Surface finishing techniques like anodizing, powder coating, or shot blasting may also be used to improve corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
Benefits of Aluminum Hot Forging
Hot forging aluminum offers several advantages over other manufacturing processes, making it the preferred choice for industries that require high-strength and precision-engineered components. The key benefits include:
Enhanced Mechanical Properties
One of the biggest advantages of aluminum hot forging is the improved strength and durability of the final component. The grain structure of aluminum is refined during the forging process, resulting in higher tensile strength, better fatigue resistance, and improved impact toughness compared to cast or machined parts.
Lightweight and High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Aluminum is known for its lightweight properties, making it ideal for applications where weight reduction is crucial, such as aerospace and automotive industries. Forged aluminum components provide the perfect balance of strength and weight, helping improve fuel efficiency and performance in vehicles and aircraft.
Superior Structural Integrity
Unlike casting or welding, which may introduce porosity or weak points in a component, hot forging aluminum produces parts with excellent structural integrity. The absence of internal defects ensures better performance and longer service life.
Cost-Effective Production
Although hot forging requires specialized equipment and skilled labor, it offers cost savings in the long run. The process minimizes material waste and reduces the need for extensive machining, lowering overall production costs while ensuring high-quality components.
Improved Wear and Corrosion Resistance
Aluminum hot forging components often undergo additional treatments to enhance their wear and corrosion resistance. This makes them ideal for harsh environments, including marine, automotive, and industrial applications.
Applications of Aluminum Hot Forging
Aluminum hot forging is used across various industries to produce critical components that require strength, precision, and durability. Some common applications include:
Aerospace Industry
Forged aluminum components are widely used in aerospace applications due to their lightweight nature and high strength. Aircraft structural parts, engine mounts, landing gear components, and control system parts are commonly manufactured using aluminum hot forging.
Automotive Industry
The automotive sector relies heavily on hot forging aluminum to produce durable and lightweight parts that enhance fuel efficiency and vehicle performance. Components such as suspension arms, steering knuckles, transmission housings, and engine brackets benefit from the strength and reliability of forged aluminum.
Industrial and Machinery Applications
Heavy machinery, industrial equipment, and construction tools require robust and long-lasting parts. Aluminum hot forging is used to manufacture components such as gears, hydraulic fittings, flanges, and machine tool parts that can withstand high loads and harsh operating conditions.
Medical Equipment
The medical industry also benefits from aluminum hot forging due to the metal’s biocompatibility and resistance to corrosion. Surgical instruments, prosthetic components, and imaging equipment parts often incorporate precision-forged aluminum for enhanced performance and reliability.
Electrical and Electronics
Aluminum’s excellent thermal and electrical conductivity makes it a preferred material for electrical components. Heat sinks, connectors, and enclosures for electronic devices are often produced using aluminum hot forging to ensure efficiency and longevity.
Challenges in Aluminum Hot Forging
Despite its numerous advantages, aluminum hot forging presents some challenges that manufacturers must address to achieve optimal results. Some of these challenges include:
Temperature Control
Maintaining the correct forging temperature is critical to preventing defects such as cracking, warping, or improper grain structure formation. Strict temperature monitoring and control are required throughout the process.
Die Wear and Maintenance
Forging dies experience significant stress and wear over time, especially when working with aluminum alloys with high strength. Regular die maintenance and replacement are necessary to maintain precision and consistency in forged components.
Post-Forging Machining
While hot forging reduces the need for extensive machining, some components may still require precision CNC machining to meet tight tolerances. This adds an extra step to the production process but ensures superior quality and dimensional accuracy.
Future Trends in Aluminum Hot Forging
As industries continue to demand high-performance and sustainable manufacturing solutions, advancements in aluminum hot forging technology are shaping the future of the industry. Some emerging trends include:
Automation and Industry 4.0 Integration
The integration of automation, robotics, and smart monitoring systems is enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of the aluminum hot forging process. Real-time data collection and AI-driven optimizations are helping manufacturers improve production speed and reduce defects.
Advanced Alloy Development
New aluminum alloys with enhanced properties, such as increased heat resistance and improved strength-to-weight ratios, are being developed to meet the evolving demands of aerospace, automotive, and industrial applications.
Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
As environmental concerns grow, manufacturers are adopting more sustainable practices in hot forging aluminum. Recycling aluminum scrap, reducing energy consumption, and implementing eco-friendly heat treatment methods are becoming standard practices in the industry. Aluminum hot forging remains a vital manufacturing process for producing high-strength, lightweight, and durable components across multiple industries. By understanding the process, benefits, and challenges, businesses can make informed decisions to optimize their production strategies. As advancements in automation, materials, and sustainability continue to shape the industry, the future of aluminum hot forging looks promising for manufacturers looking to enhance efficiency and innovation.
Innovations Driving the Future of Aluminum Hot Forging
The aluminum hot forging industry is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements, increasing demand for lightweight materials, and the need for cost-effective manufacturing solutions. Innovations in forging techniques, material science, and digital manufacturing are shaping the future of aluminum hot forging.
AI and Machine Learning in Forging Processes
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are playing a crucial role in optimizing aluminum hot forging operations. Smart algorithms can analyze forging parameters in real-time, adjust press settings, and predict potential defects before they occur. By leveraging AI-driven analytics, manufacturers can improve process efficiency, reduce waste, and ensure consistent product quality.
3D Printing and Hybrid Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, is being integrated with traditional hot forging processes to create complex and highly optimized aluminum components. Hybrid manufacturing, which combines forging with 3D-printed preforms, allows manufacturers to produce near-net-shape parts, reducing material waste and machining time. This innovation is particularly beneficial for industries requiring lightweight and high-performance parts, such as aerospace and automotive.
Advanced Heat Treatment Techniques
New heat treatment methods are enhancing the mechanical properties of aluminum hot forging components. Controlled atmosphere furnaces and induction heating technologies provide precise temperature control, ensuring uniform hardness, strength, and resistance to thermal fatigue. Advanced quenching techniques, such as cryogenic treatment, are also being used to further enhance material toughness and wear resistance.
Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Forging
Sustainability is becoming a major focus in the aluminum hot forging industry. Manufacturers are implementing energy-efficient furnaces, using renewable energy sources, and adopting closed-loop recycling systems to minimize waste. Additionally, advancements in lubricant-free forging and eco-friendly coatings are reducing the environmental impact of aluminum forging operations.
Key Considerations When Choosing an Aluminum Hot Forging Manufacturer
Selecting the right aluminum hot forging manufacturer is critical to ensuring the quality, performance, and cost-effectiveness of forged components. Businesses should consider several factors when choosing a forging partner.
Expertise and Experience
A manufacturer with extensive experience in aluminum hot forging can provide valuable insights, optimize the forging process, and ensure consistent quality. Companies with a proven track record in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical manufacturing are more likely to deliver high-performance forged components.
Material Selection and Alloy Capabilities
Different applications require specific aluminum alloys with varying properties. A reliable forging manufacturer should offer a wide range of alloy options and provide guidance on selecting the best material for a given application. Common aluminum alloys used in hot forging include:
- 6061 Aluminum: Known for its excellent strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability.
- 7075 Aluminum: A high-strength alloy often used in aerospace and high-performance automotive applications.
- 2024 Aluminum: Offers high fatigue resistance and is commonly used in aircraft structures.
Quality Control and Certifications
Stringent quality control measures are essential for ensuring the reliability and durability of aluminum hot forging components. Businesses should look for manufacturers with ISO 9001, AS9100 (for aerospace applications), or IATF 16949 (for automotive manufacturing) certifications. These standards ensure that the manufacturer follows strict quality management practices.
Production Capacity and Lead Times
The ability to meet production deadlines is crucial, especially for industries with tight supply chain schedules. Companies should assess a manufacturer’s production capacity, lead times, and ability to scale production as demand fluctuates.
Secondary Operations and Value-Added Services
Many aluminum hot forging manufacturers offer additional services such as CNC machining, heat treatment, surface finishing, and assembly. Choosing a manufacturer that provides comprehensive services can streamline production and reduce overall costs.
Emerging Applications of Aluminum Hot Forging
As industries continue to demand lightweight, strong, and durable materials, aluminum hot forging is expanding into new and innovative applications.
Electric Vehicles (EVs)
The rise of electric vehicles has created a growing demand for lightweight and high-strength aluminum components. Hot forged aluminum parts, such as battery enclosures, suspension arms, and drivetrain components, are helping automakers improve energy efficiency and vehicle performance.
Renewable Energy
Aluminum hot forging is playing a key role in the renewable energy sector. Forged aluminum components are used in wind turbines, solar panel mounts, and hydroelectric power systems due to their corrosion resistance and structural integrity.
Defense and Military Applications
The defense industry relies on aluminum hot forging for the production of military-grade components, including armor plating, weapon system mounts, and aircraft structures. The strength-to-weight ratio of forged aluminum is critical for enhancing mobility and durability in defense applications.
High-Performance Sports Equipment
Hot forged aluminum is increasingly used in high-performance sports equipment such as bicycle frames, racing car components, and professional-grade tools. The combination of lightweight properties and superior strength makes aluminum an ideal material for sports engineering.
Conclusion
Aluminum hot forging remains a vital manufacturing process for producing high-strength, lightweight, and durable components across multiple industries. With advancements in AI-driven automation, hybrid manufacturing, sustainable practices, and high-performance materials, the future of aluminum hot forging is brighter than ever. By choosing the right manufacturer, optimizing production techniques, and adopting innovative technologies, businesses can maximize the benefits of aluminum hot forging. Whether in aerospace, automotive, renewable energy, or defense, forged aluminum components will continue to drive efficiency, performance, and sustainability in modern manufacturing. Additionally, aluminium die casting complements hot forging by providing manufacturers with alternative methods for producing complex, high-precision aluminum parts. The combination of both processes enables companies to achieve optimal performance, cost-efficiency, and material utilization in various applications.
Recent Comments