Injection molding is a popular manufacturing process used to produce high volumes of identical parts. One of the critical components of injection molding is the runner system, which is responsible for channeling the molten material from the injection molding machine to the mold cavities. The cold runner mold is a specific type of runner system in which the material within the runner does not require heating to remain in a liquid state. Cold runner systems are commonly used in manufacturing processes due to their simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and ease of use. A cold runner system refers to a runner that remains at ambient temperature, in contrast to the hot runner system, which actively maintains a heated state to keep the material molten. In a cold runner mold, the material solidifies within the runner as it cools, which can increase the production cycle time but offers advantages such as lower system complexity and reduced tooling costs.
Understanding the role of the cold runner mold in the injection molding process is essential for manufacturers who need to decide between using cold runner or hot runner systems based on the requirements of their parts, production volumes, and cost considerations.
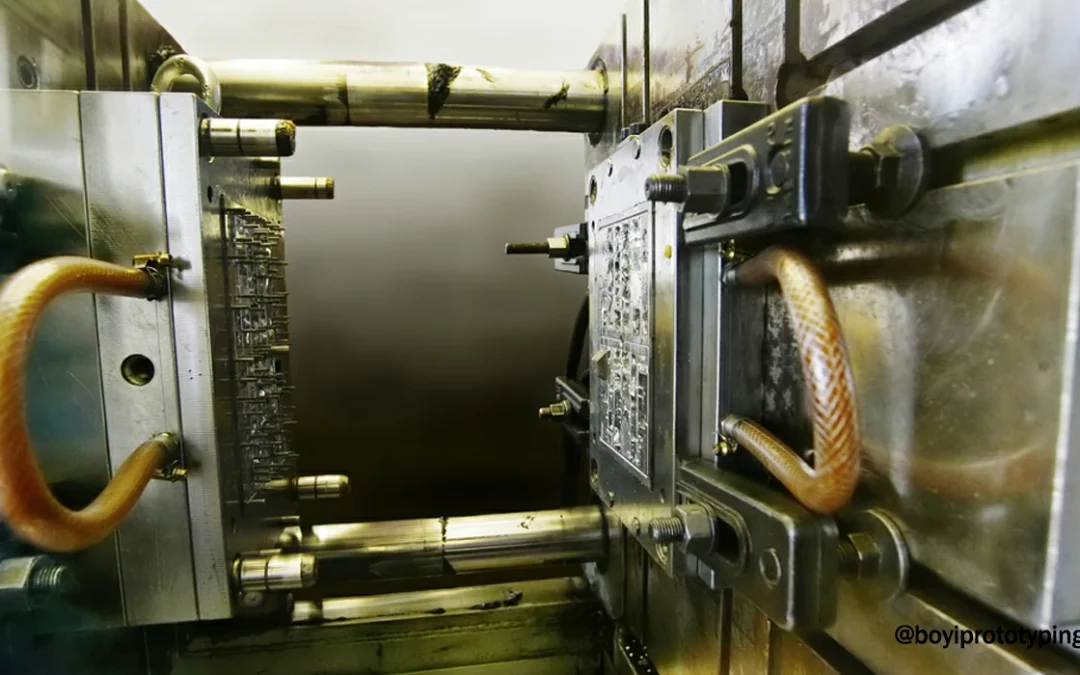
Cold Runner Injection Molding Process
Cold runner injection molding is a process that involves the use of a cold runner system to channel the molten material to the cavities of the mold. The molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity through the cold runner, where it cools and solidifies before being ejected. The cold runner system includes channels or passages that lead the material into the mold. Unlike a hot runner system, the cold runner is not heated, meaning the material in the runner cools and solidifies before the molded part is ejected from the cavity. This process is ideal for products that do not require extremely high cycle times or the need for high-precision molding. Cold runner molds are often used in the production of parts that can withstand some level of scrap material or that do not have complex geometries. The cooled runner material typically solidifies and is either removed and discarded or reused in future production runs.
Advantages of Cold Runner Injection Molding
- Simplicity and Cost-Effectiveness One of the most significant advantages of using a cold runner system is its simplicity. The absence of heating elements means that the mold design is less complicated, and the overall system is less expensive. The cost savings associated with cold runner injection molding make it a preferred choice for manufacturers on a budget or those working with lower-volume production runs.
- Lower Tooling Costs Since cold runner molds do not require temperature control or heating systems, they tend to be less costly to design and manufacture. This can be especially advantageous when creating prototypes or parts in smaller quantities, where the cost of a hot runner system may not be justifiable.
- Easier Maintenance Cold runner molds are simpler to maintain because they lack the complexity of hot runner systems. The lack of electrical components or heating elements means there are fewer opportunities for system malfunctions. Maintenance is generally quicker and more cost-effective, resulting in lower downtime during production.
- Waste Reduction Cold runner injection molding allows for the potential recycling of scrap material. While some runners may become solidified and unusable, excess material that solidifies can be ground up and reused in subsequent runs, contributing to cost savings and waste reduction. The material can be collected, cleaned, and reused, especially for certain types of plastics.
- Versatility for Certain Applications Cold runner molds can be ideal for applications where precise control of the material is not as critical. For products that do not require extremely tight tolerances or complex geometries, cold runner injection molding can provide an efficient and reliable manufacturing solution.
Cold Runner vs Hot Runner Injection Molding
When comparing cold runner to hot runner injection molding, it’s essential to consider the specific needs of the project, such as the complexity of the part, production volume, and the material being used. Both runner systems have their benefits, but they are best suited for different situations.
Cold Runner Injection Molding
In cold runner systems, the runner channels remain at room temperature, and the plastic material cools and solidifies in the runner as the part is molded. The solidified material must then be removed before the next injection cycle. Cold runner systems are generally better suited for lower-volume production and less intricate part designs.
Pros of Cold Runner Molding:
- Simpler and cheaper tooling design
- Reduced maintenance costs
- No need for temperature controls
- Ideal for smaller production runs
- Recyclable scrap material
Cons of Cold Runner Molding:
- Increased material waste, as the solidified runner must be discarded or recycled
- Longer cycle times due to cooling and solidification in the runner
- Higher waste rates in certain materials or parts
- May not be suitable for high-precision, high-volume production
Hot Runner Injection Molding
Hot runner injection molding involves the use of heated runner systems, where the plastic material remains molten as it moves through the runner and enters the mold cavity. The heating elements are strategically placed to prevent the material from cooling before reaching the cavity, ensuring faster cycle times and better control over the material flow. Hot runner systems are typically more expensive but are often used in high-volume production or when intricate parts require precise material flow.
Pros of Hot Runner Molding:
- Faster cycle times due to the absence of cooling and solidification in the runner
- Less material waste, as the runners remain molten and are recycled back into the system
- Ideal for high-volume, high-precision manufacturing
- Can be more energy-efficient when producing large volumes of parts
Cons of Hot Runner Molding:
- Higher tooling costs due to the complexity of the system
- Increased maintenance costs due to the heating elements
- More complex system design and control requirements
- Higher upfront investment for hot runner systems
When to Choose Cold Runner vs Hot Runner
- For Low-Volume Production: Cold runner systems are ideal when producing lower quantities of parts. The simplicity and lower tooling costs make them the better option when the volume of parts does not justify the expense of a hot runner system.
- For High-Volume Production: Hot runner systems are better suited for high-volume runs because they offer faster cycle times and reduced material waste. They are commonly used in the mass production of parts with intricate designs or high precision.
- For Parts with Simple Geometries: If the parts being produced have relatively simple shapes and do not require high precision or short cycle times, a cold runner system is a cost-effective and efficient solution.
- For Complex and Detailed Parts: Hot runner systems excel in applications that require precise control over the flow of molten plastic and intricate designs. If the part geometry is complex, requiring multiple cavities or undercuts, a hot runner system may be the better choice.
Injection Molding Cold Runner: How It Works
In injection molding, the cold runner system consists of channels that carry molten plastic to the mold cavities. The runner channels themselves cool down quickly, which can result in material solidification within the runner before the part has been ejected. The solidified material must then be removed and discarded, though in some cases, it can be recycled.
During the injection molding process, the material is injected into the cold runner channels and pushed into the mold cavity. Once the plastic fills the cavity, the mold is cooled to solidify the material. After cooling, the mold opens, and the part is ejected, leaving behind the runner material. The runner system then either must be discarded or reused in subsequent batches.
The most common materials used in cold runner systems are thermoplastics, such as polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene, and ABS, as these materials are relatively easy to cool and solidify. The mold design and the choice of material are key factors that influence the overall performance of the cold runner system.
Benefits of Cold Runner Injection Molding
- Lower Upfront Investment: Cold runner molds are less expensive to design and manufacture than hot runner molds, making them an attractive option for startups or manufacturers with limited budgets.
- Simplicity in Design and Maintenance: With fewer components and no need for temperature control, cold runner molds are simpler and more reliable, leading to less maintenance and fewer potential issues with malfunctioning heating systems.
- Material Flexibility: Cold runner systems work well with a wide variety of thermoplastics, making them ideal for use with materials that do not require tight temperature control during the molding process.
- Recycling of Scrap: Solidified runners can be recycled, allowing manufacturers to reduce waste and reuse plastic materials, ultimately lowering costs over time.
Further Insights on Cold Runner Injection Molding and Its Applications
As the manufacturing landscape continues to evolve, cold runner injection molding stands out as a versatile and cost-effective option for many industries. In this section, we will explore additional benefits, considerations, and real-world applications of cold runner injection molding. Furthermore, we will discuss the increasing role of global production, particularly in markets like China, and how it impacts the cold runner injection molding industry.
Material Choices in Cold Runner Injection Molding
One of the key factors that influence the performance of cold runner injection molding is the selection of materials. Different thermoplastics and elastomers behave differently when subjected to the injection molding process. Cold runner molds are typically used for thermoplastic materials because they solidify more quickly and are easier to handle in a system where the runner is not heated.
Commonly used materials in cold runner injection molding include:
- Polyethylene (PE): A widely used thermoplastic, PE is durable, flexible, and easy to mold. It is commonly used in packaging, household items, and toys.
- Polypropylene (PP): Another versatile thermoplastic, PP is known for its resistance to chemical reactions and its high melting point. It is commonly used in automotive parts, containers, and medical equipment.
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): ABS is known for its toughness, impact resistance, and ease of molding. It is used in automotive parts, electronic housings, and consumer products.
- Polystyrene (PS): Polystyrene is often used in the production of inexpensive consumer goods like plastic cutlery, containers, and packaging.
The choice of material depends on several factors, such as the desired properties of the final product (e.g., strength, flexibility, or chemical resistance), the specific molding application, and cost considerations. For example, manufacturers using cold runner systems for high-volume production will often select materials that are easy to handle and quick to solidify, such as PP or PE.
Cold Runner Molds for Large and Small Parts
Cold runner injection molding is flexible enough to handle both large and small parts, but different considerations apply when designing molds for parts of varying sizes. For small parts, the cold runner system is typically more straightforward, requiring fewer material channels and less complexity in the design of the runner system.
On the other hand, large parts may require larger molds and multiple cavities, which can increase the complexity of the cold runner system. In these cases, manufacturers need to carefully design the runners to ensure efficient material flow and to minimize the chances of defects such as short shots, warping, or uneven material distribution.
For instance, when producing large automotive parts or home appliances, manufacturers must ensure that the cold runner channels are designed with the right cross-sectional area to allow the molten plastic to flow evenly through the mold. If the runner system is poorly designed for large parts, it can result in longer cycle times or incomplete fills, both of which can be detrimental to the production process.
Mold Design Considerations for Cold Runner Systems
Mold design is crucial to the success of any injection molding process, and cold runner systems are no exception. Proper design ensures that material flows smoothly into the mold cavity, reducing the risk of defects, waste, and inefficiencies.
Key considerations in cold runner mold design include:
- Runner Size: The size of the runner must be appropriately matched to the material and the part being molded. Too small a runner can cause material flow issues, while too large a runner can result in excess material waste.
- Flow Balance: Ensuring that material flows evenly into each mold cavity is important for achieving consistent part quality. Flow balance can be affected by runner length, diameter, and gating design.
- Ventilation: Proper ventilation is necessary to allow air to escape the mold as it fills, preventing issues like air pockets or incomplete fills. Inadequate ventilation can lead to defects in the molded parts, such as voids or sink marks.
- Cooling Channels: The design of cooling channels within the mold is vital for maintaining the temperature of the mold and the plastic during the injection molding process. For cold runner systems, it’s especially important to ensure that the cooling channels are properly positioned to cool both the mold cavities and the runners effectively.
- Gating Design: Gates are the points where the molten material enters the mold cavity. In cold runner injection molding, the design of the gates is particularly important, as poorly designed gates can cause uneven filling or excessive material waste.
- Ejector System: The ejector system is responsible for removing the molded part from the mold once it has cooled. A well-designed ejector system helps ensure that the part is ejected without damaging it and without excessive force.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
In today’s world, manufacturers are increasingly looking for ways to reduce their environmental impact. Cold runner injection molding can play a significant role in sustainability efforts, especially with the ability to recycle scrap material.
One of the challenges of injection molding is the material waste produced by the runner system. In traditional molding systems, the runner channels must be removed and discarded. However, with cold runner injection molding, scrap material from the runner can often be reused by grinding it down and adding it back into the production process. This can reduce overall material waste and help manufacturers reduce the need for virgin materials, which can have a significant environmental impact.
Some manufacturers also use biodegradable or recyclable materials in their cold runner molding processes to further reduce waste and environmental impact. The choice of material is crucial in achieving a balance between the benefits of the molding process and the sustainability of the final product.
The Role of Cold Runner Injection Molding in Global Manufacturing
The demand for high-quality plastic parts produced through injection molding has led to an expansion in manufacturing capabilities worldwide. One country where cold runner injection molding has seen significant growth is China. As one of the world’s largest manufacturers, China has a vast number of mold factories, many of which specialize in injection molding techniques, including cold runner systems.
A mold factory in China can offer significant advantages, such as cost-effectiveness, high production capacity, and expertise in a wide range of injection molding processes. Chinese mold makers are known for their ability to provide high-quality molds at competitive prices, making them a popular choice for global companies seeking to reduce manufacturing costs. Furthermore, the country’s vast network of suppliers and manufacturers allows for quick turnaround times, making it easier to meet tight deadlines for production runs.
The combination of affordability, expertise, and rapid production has made China a major player in the global injection molding market. Manufacturers looking to create plastic components for various industries—whether automotive, electronics, or consumer goods—often turn to Chinese mold factories to meet their production needs.
Cost-Effectiveness of Cold Runner Injection Molding
One of the key reasons cold runner injection molding remains a popular choice is its cost-effectiveness. As previously mentioned, cold runner systems are less complex and require fewer components than hot runner systems, which translates to lower initial setup and tooling costs. These cost savings make cold runner systems ideal for small to medium-sized production runs, where the higher costs associated with hot runner systems may not be justified.
In addition to the lower upfront costs, cold runner systems offer cost savings through efficient material use. While scrap material is produced in the runner system, much of it can be reused in future production cycles, reducing the need for new materials. This helps to further lower overall manufacturing costs and improve the efficiency of the production process.
Applications in Various Industries
Cold runner injection molding finds applications in many industries due to its versatility and ability to produce high-quality plastic parts at an affordable cost. Some of the industries that commonly use cold runner injection molding include:
- Automotive: The automotive industry relies on injection molding for producing parts like bumpers, dashboards, interior components, and exterior trim. Cold runner injection molding is often used for these parts when cost is a critical factor, and the parts have relatively simple geometries.
- Consumer Electronics: Electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, and home appliances often require molded plastic components for housings, buttons, and other structural elements. Cold runner systems are commonly used for parts that don’t require high-precision molding.
- Medical Devices: The medical industry frequently uses injection molding for creating components like syringes, medical trays, and equipment housings. Cold runner injection molding is often selected for these applications due to its cost-effectiveness and material handling capabilities.
- Packaging: Cold runner molding is widely used in packaging applications such as bottle caps, containers, and lids. The relatively simple design of these items makes cold runner systems an excellent choice for high-volume production runs.
Conclusion
Cold runner injection molding remains a critical part of the manufacturing process, offering numerous benefits in terms of cost savings, simplicity, and flexibility. As manufacturers continue to seek efficient and cost-effective solutions for producing high-quality plastic parts, the use of cold runner systems will continue to thrive. The ability to recycle material and the potential for applications across various industries further enhances the value of this process. The rise of global manufacturing, particularly in markets such as China, has further bolstered the appeal of cold runner injection molding, allowing businesses worldwide to access affordable and efficient production solutions. Whether it’s automotive parts, consumer electronics, or medical devices, cold runner injection molding offers a practical, sustainable, and cost-effective approach to high-quality plastic manufacturing.
Recent Comments